Overview
Author: Diyaa
Published date: August 3rd, 2024
Last updated: August 18th, 2024
This article explains how to utilize Policy Based Routing (PBR) to a remote cloud virtual private server over a WireGuard VPN tunnel in Pfsense. This will allow for the setup of custom specific host default route modification based on the policy based routing policies.
WARNING
I am using nftables in this setup. Installing nftables over iptables might override your iptables ruleset.
I am using the range of 198.51.100.0/30 on the VPN tunnel between the VPS and Pfsense. Just in case you are asking “Isn’t that a public IP?“. Review RFC5737 for more information about documentation IP ranges.
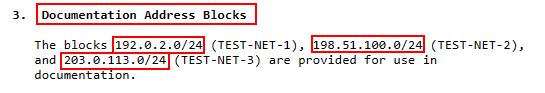
I am also doing MSS clamping to ensure that the TCP segment size does not exceed the value of the MTU on the WireGuard VPN tunnel. What is MSS clamping you ask? Review RFC4459 for more information on MSS clamping.

Diagram:
This is a diagram overview of what will be configured by following the steps in this article.
VPS setup:
Install Required Packages:
Install all the required packages on your VPS.
sudo apt update; sudo apt upgrade -y; \
sudo apt install ssh wireguard nftables coreutils -yEnable IP Forwarding:
Add the IP forwarding kernel module:
echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.confApply kernel modules:
sudo sysctl -pNftables Ruleset:
Place the config below in the following file /etc/nftables.conf.
Warning:
I would recommend you avoid using the default WireGuard port. In the event there is a WireGuard exploit in the future someone could run it against all public IPs on the default port. The WireGuard default port is
51820
IMPORTANT
Change the following parameters to meet your needs:.
DEV_WORLD: The WAN interface of the VPS. You will need to find what interface on your VPS has a public IP on it.Local_Networks: The ranges of your local network behind your Pfsense router. You can seperate multiple ranges with a comma.SSH_In_Port: SSH port to allow through nftables ruleset. Not adding this means you won’t be able to SSH into your VPS instance.WireGuard_In_Port: The WireGuard port to listen on from WAN. I recommend changing this to anything other than the default port (default port is 51820).IPv4_DEV_WireGuard_MSS: This is the Maximum Segment Size (MSS) value that will be set for outbound TCP connections.
Nftables configuration:
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
flush ruleset
## Change the values below to meet your needs:
# VPN Interface
define DEV_WireGuard = wg0
# WAN Interface
define DEV_WORLD = enp1s0
# Local networks from the wireguard tunnel
define Local_Networks = { 10.0.0.0/8 }
# SSH port
define SSH_In_Port = 22
# WAN inbound Wireguard port
define WireGuard_In_Port = 60000
# MSS override
# Note: This is assuming that you are using an MTU value of 1420 on the WireGuard tunnel interface.
define IPv4_DEV_WireGuard_MSS = 1380
##########################################
#### Don't edit anything below this line.#
##########################################
table inet global {
chain inbound_world {
# allow SSH connections from internet host.
tcp dport $SSH_In_Port accept
# allow wireguard connections from the internet.
udp dport $WireGuard_In_Port accept
}
chain inbound_private_lan {
# accepting ping (icmp-echo-request) for diagnostic purposes. I prefer allowing ping from inside the tunnel only.
icmp type echo-request limit rate 10/second accept
# allow SSH connections from the wireguard tunnel.
tcp dport $SSH_In_Port accept
}
chain inbound {
type filter hook input priority 0; policy drop;
# Allow traffic from established and related packets, drop invalid
ct state vmap { established : accept, related : accept, invalid : drop }
# allow loopback traffic, anything else jump to chain for further evaluation
iifname vmap { lo : accept, $DEV_WORLD : jump inbound_world, $DEV_WireGuard : jump inbound_private_lan }
# the rest is dropped by the above policy
}
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority 0; policy drop;
# MSS clamping
iifname $DEV_WORLD oifname $DEV_WireGuard ip daddr $Local_Networks tcp flags syn tcp option maxseg size set $IPv4_DEV_WireGuard_MSS counter
# Allow traffic from established and related packets, drop invalid
ct state vmap { established : accept, related : accept, invalid : drop }
# connections from the internal net to the internet: Malicious to WAN allowed; WAN to Malicious not allowed
meta iifname . meta oifname { $DEV_WireGuard . $DEV_WORLD, $DEV_WORLD . $DEV_WireGuard } accept
# the rest is dropped by the above policy
}
chain output {
type filter hook output priority filter; policy accept;
# Accept and counter outbound traffic
counter accept
}
chain input {
type nat hook prerouting priority -100; policy accept;
# Destination NAT
}
chain outgoing {
type nat hook postrouting priority 100; policy accept;
# NAT Masquerade private IP addresses when forwarding traffic to the internet
ip saddr $Local_Networks meta oifname $DEV_WORLD counter masquerade random,persistent
}
}Apply the nftables ruleset:
NOTE
You might face an error where nftables is unable to restart. This can happen if the kernel module for NAT masquerade is not loaded. You just need to reboot your instance
sudo reboot nowand that should fix the issue.
sudo systemctl enable --now nftables; sudo systemctl reload nftablesWireGuard Setup:
Generate WireGuard Keys:
You can use this baby script that I made to generate all the WireGuard keys for your VPS and Pfsense router. Run the commands below in a bash shell to generate all the required WireGuard keys.
WireGuard keys generation baby script:
NOTE
You will need the values from the output of these commands later. Paste them in an empty file.
SERV_PRIV_KEY=$(wg genkey); \
SERV_PUB_KEY=$(echo "${SERV_PRIV_KEY}" | wg pubkey); \
CLIENT_PRIV_KEY=$(wg genkey); \
CLIENT_PUB_KEY=$(echo "${CLIENT_PRIV_KEY}" | wg pubkey); \
PRESHARED_KEY=$(wg genpsk); \
echo "VPS private key: ${SERV_PRIV_KEY}"; \
echo "VPS public Key: ${SERV_PUB_KEY}"; \
echo "Pfsense private key: ${CLIENT_PRIV_KEY}"; \
echo "Pfsense public Key: ${CLIENT_PUB_KEY}"; \
echo "Preshared Key: ${PRESHARED_KEY}"VPS WireGuard Configuration:
IMPORTANT
Things to change in the WireGuard configuration of the VPS:
- Be sure to change the
ListenPortvalue to match theWireGuard_In_Portvalue in the nftables rulebase configuration.- Replace the
localPrivateKeyAbcAbcAbc=value with theVPS private keyvalue from the script in the previous section.- Replace the
remotePublicKeyAbcAbcAbc=value with thePfsense public keyvalue from the script in the previous section.- Replace the
presharedkeyabcabcabc=value with thePreshared keyvalue from the script in the previous section.- The
AllowedIPsfield needs to include all the IPs that will be forwarded up the tunnel as well as the Pfsense WireGuard tunnel interface IP.
VPS WireGuard configuration:
Important:
The nftables ruleset in this guide has the WireGuard port set to
60000. You need to match your nftables ruleset value with the value in the configuration below. The value in the configuration below is namedListenPort = 60000.
[Interface]
# Name = VPS interface settings
Address = 198.51.100.1/30
ListenPort = 60000
PrivateKey = localPrivateKeyAbcAbcAbc=
MTU = 1420
[Peer]
# Name = site2.example.local
AllowedIPs = 198.51.100.2/32, 10.0.0.0/8
PublicKey = remotePublicKeyAbcAbcAbc=
PresharedKey = presharedkeyabcabcabc=Place the configuration above in the following file: /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf.
Make sure to change the permission of the WireGuard folder after you place your config in the wg0.conf file.
sudo chown root:root -R /etc/wireguard; sudo chmod 600 -R /etc/wireguardEnable and start the WireGuard tunnel:
sudo systemctl enable --now wg-quick@wg0Pfsense Configuration:
Download the WireGuard Package:
Download the WireGuard package from available packages section under the package manager in Pfsense.
Search for WireGuard and install the WireGuard package.
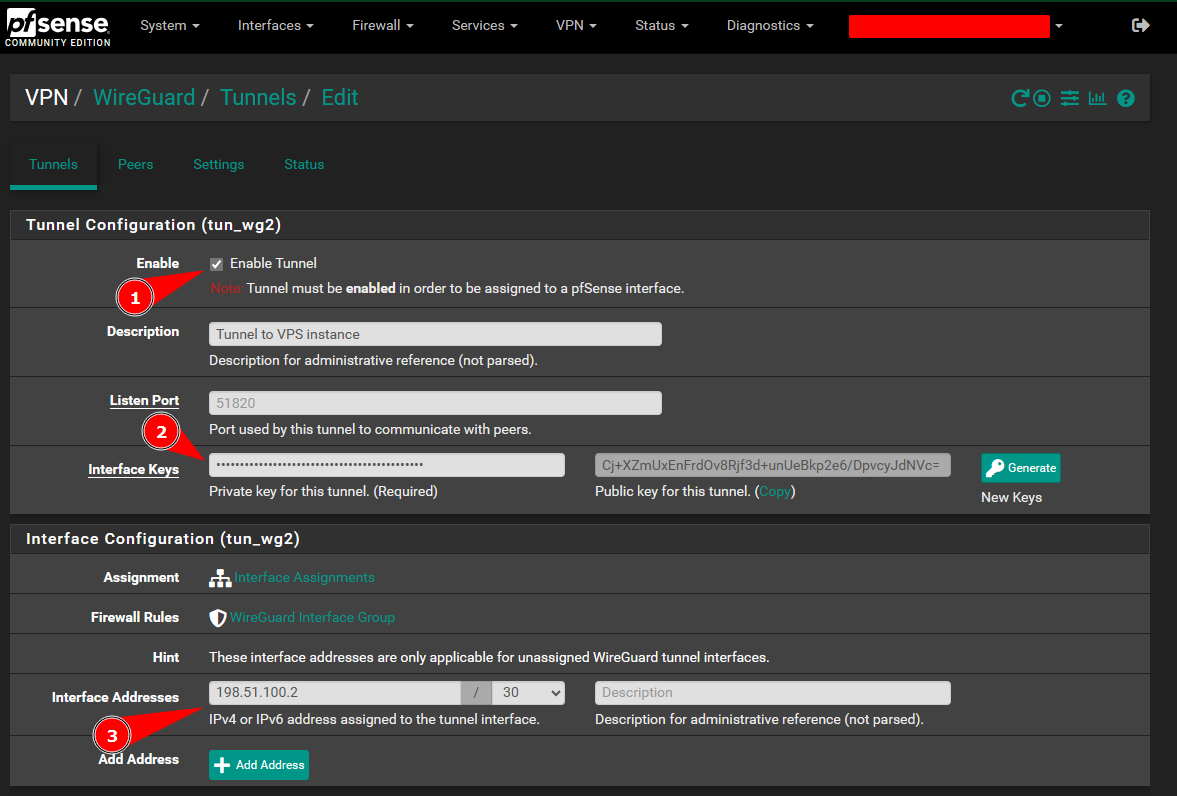
Create a New WireGuard Tunnel:
Create a new WireGuard tunnel on Pfsense:
Important:
Add the
Pfsense private keyyou generated in this step and assign the tunnel IP address.
Important:
The
Listen Portneeds to match the WireGuard port configured in the nftables ruleset.
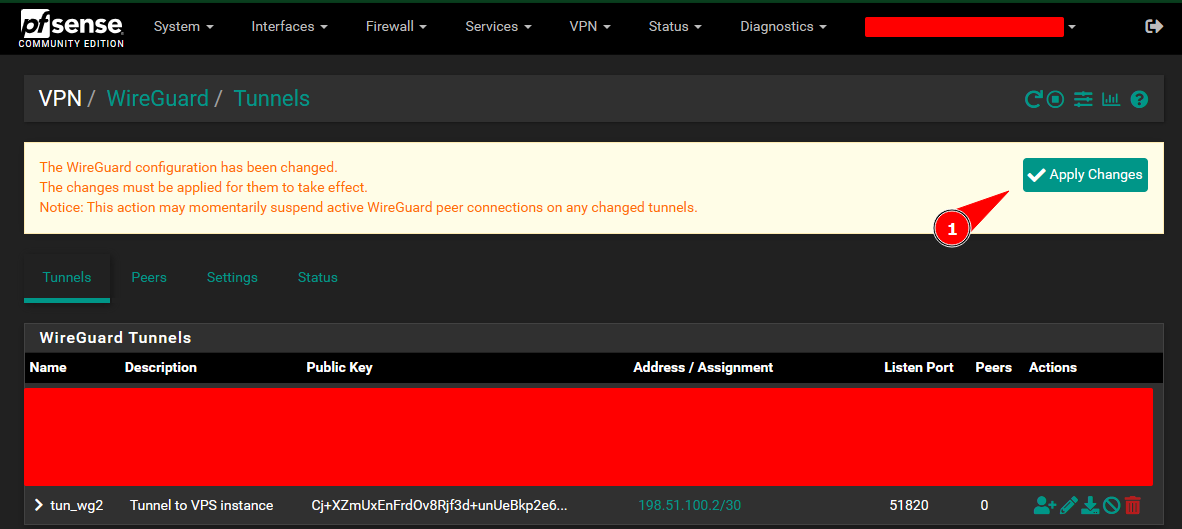
Enable The WireGuard Package:
Enable the WireGuard package:
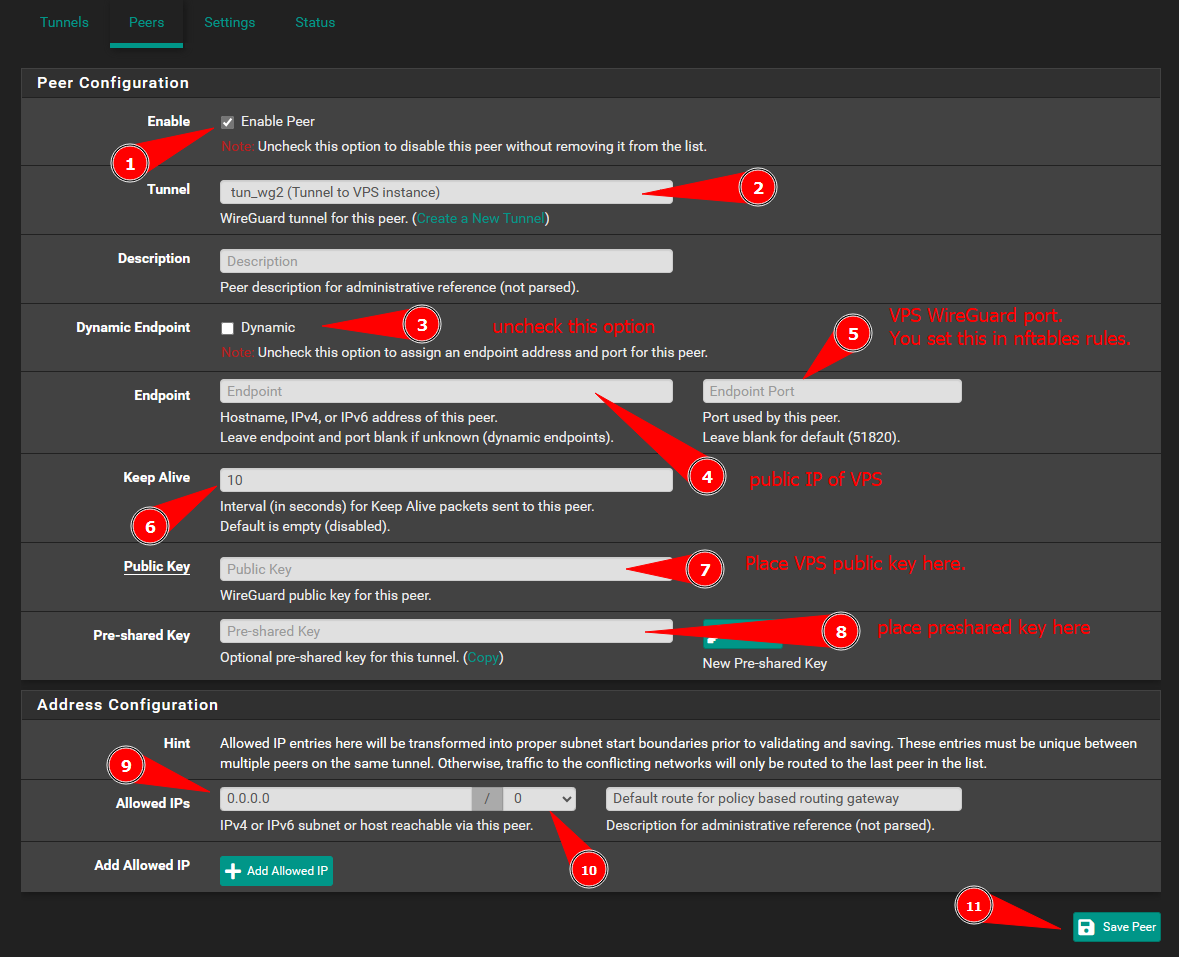
Add a Peer to The WireGuard Tunnel:
Add a peer to the tunnel:
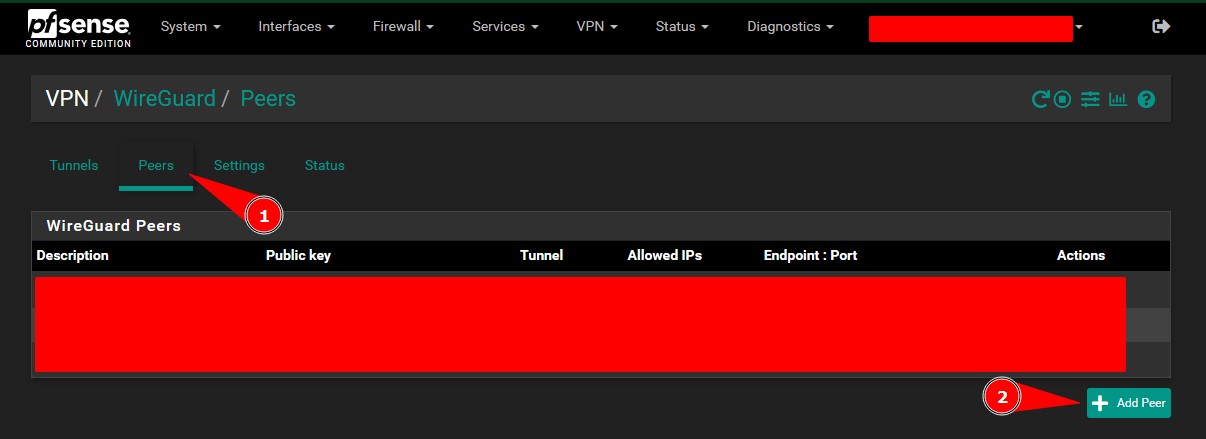
IMPORTANT
- Add the
VPS private keyyou generated in a previous step in thePublic keybox shown in the screenshot below.- Add the
Preshared keyvalue you created in a previous step in thePre-shared keybox shown in the screenshot below.
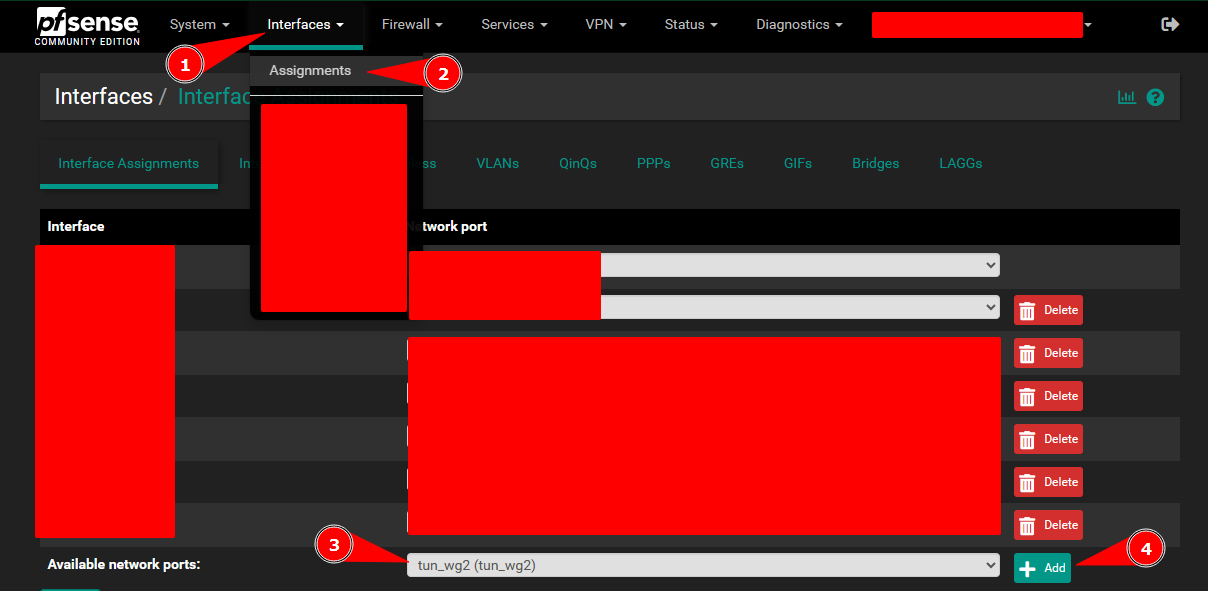
Assign The WireGuard Tunnel Interface on Pfsense:
Create a tunnel interface on Pfsense:
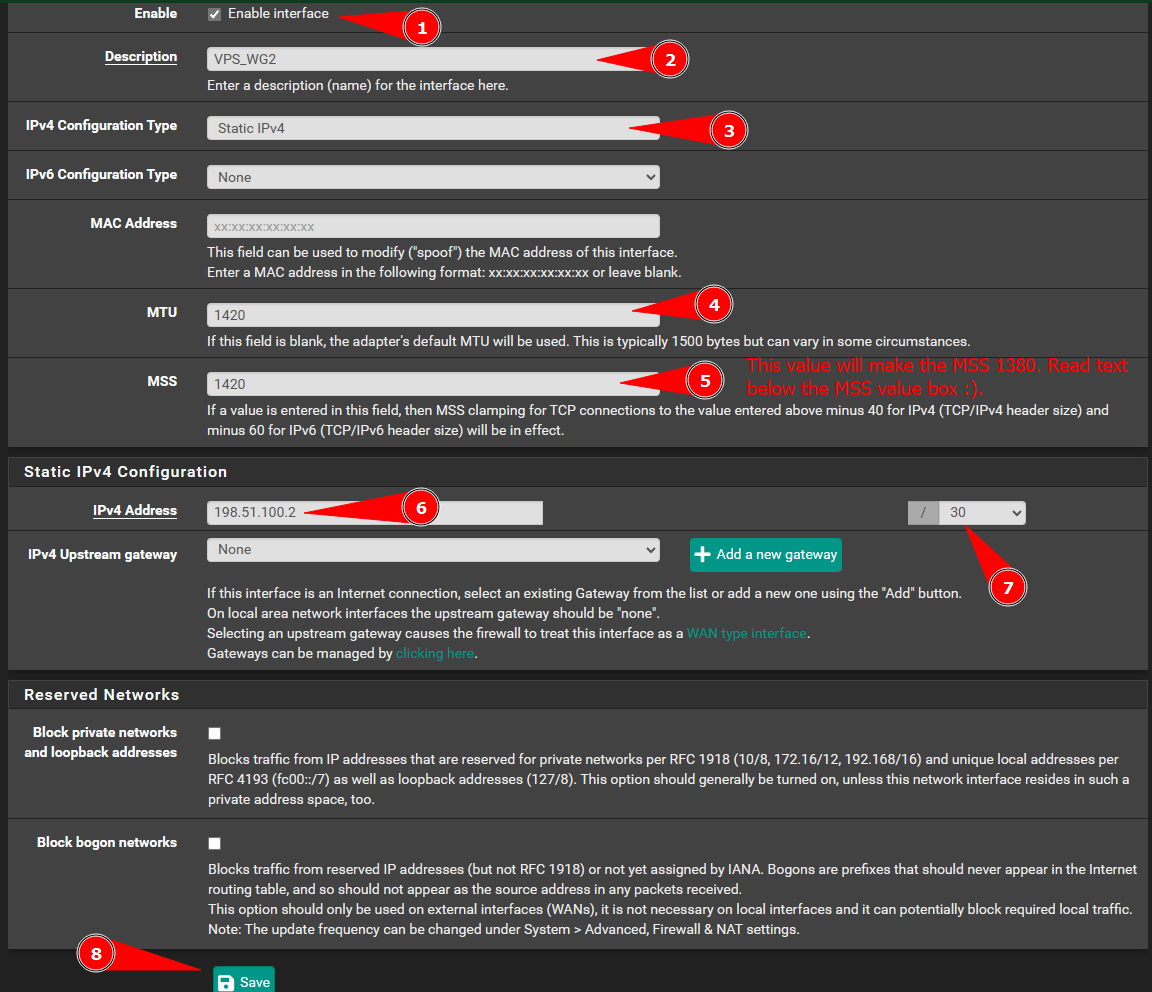
Warning
Pfsense does the calculation “automatically” based on the layer 3 protocol. Set the MSS to
1420. This will set the MSS in the TCP SYN packet to:
- 1420 - 40 = 1380 for IPv4 (20 bytes for IPv4 header and 20 bytes for TCP header)
- 1420 - 60 = 1360 for IPv6 (40 bytes for IPv6 header and 20 bytes for TCP header)
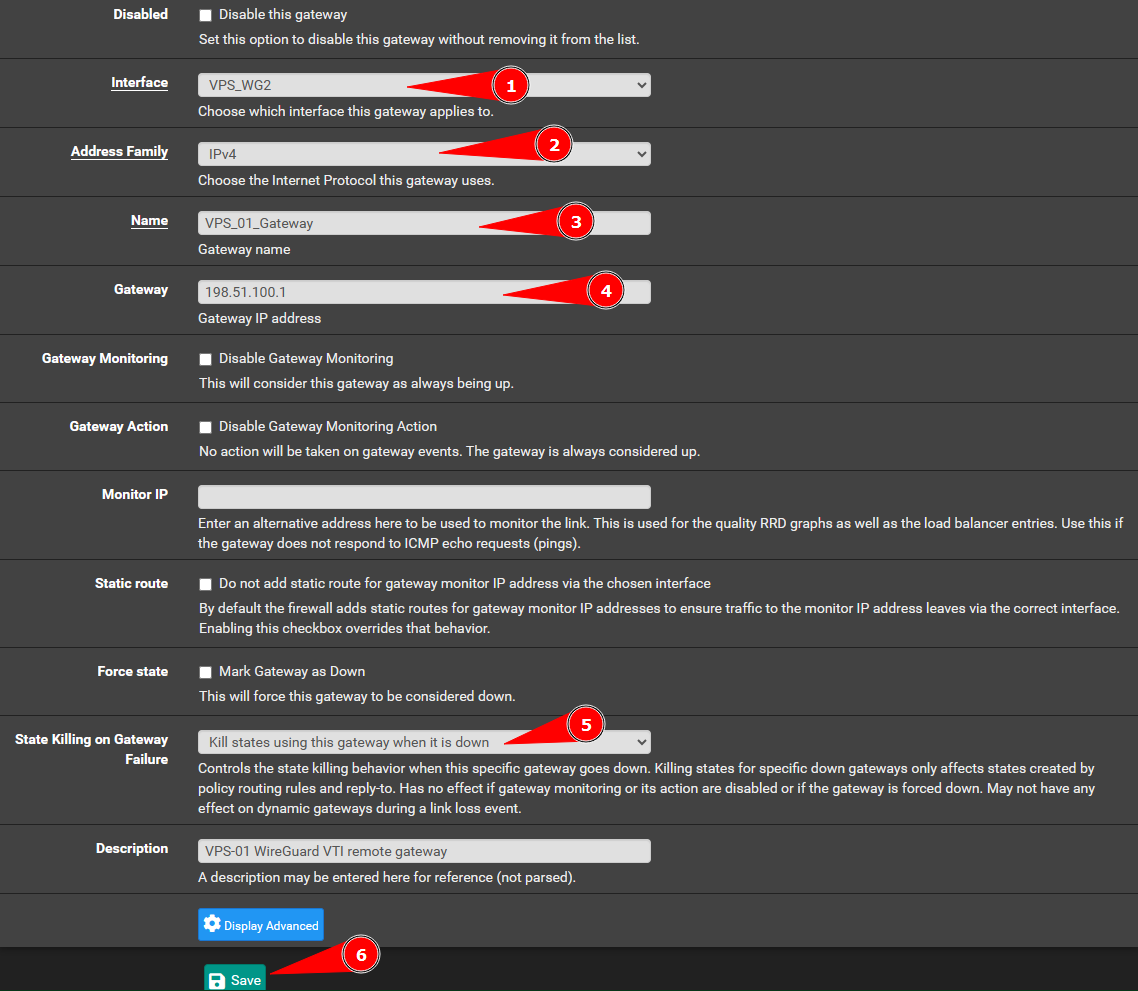
Add The VPS as a Gateway on Pfsense:
Adding a gateway of the remove VPS IP on the WireGuard interface:
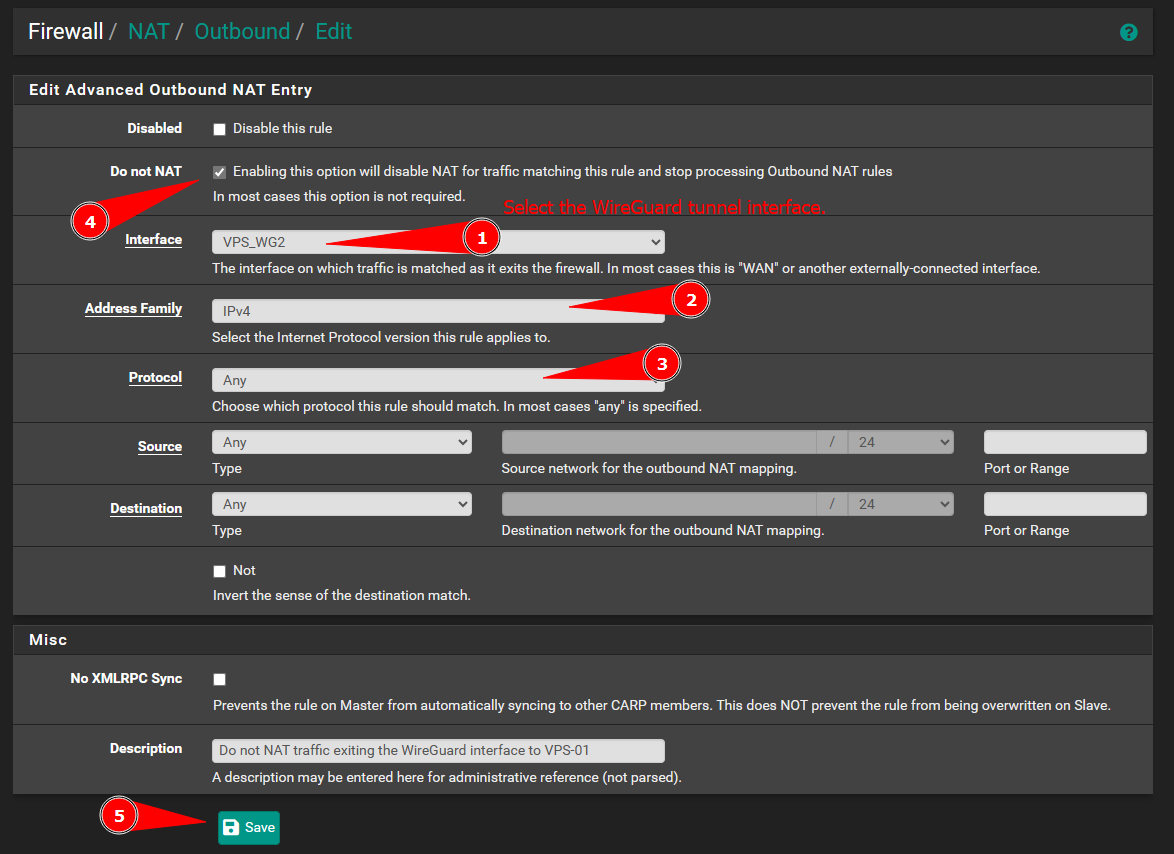
Add an Outbound “No NAT” Policy:
IMPORTANT
NAT is eval and you should try to reduce NATing as much as you can in your life. The less you NAT the less kittens die… Read this article.
Warning
I am assuming you have added your routes correctly to the
AllowedIPsfield in the WireGuard configuration on the VPS. You can not turn off NAT if your routes are not configured correctly. You can skip this step if you wish to keep murdering kittens.
NOTE
By default the outbound NAT rules are set to automatic in Pfsense. You will need to set the NAT rules to hybrid to apply manual NAT policies. The manual policies will apply before the the automatic NAT policies.
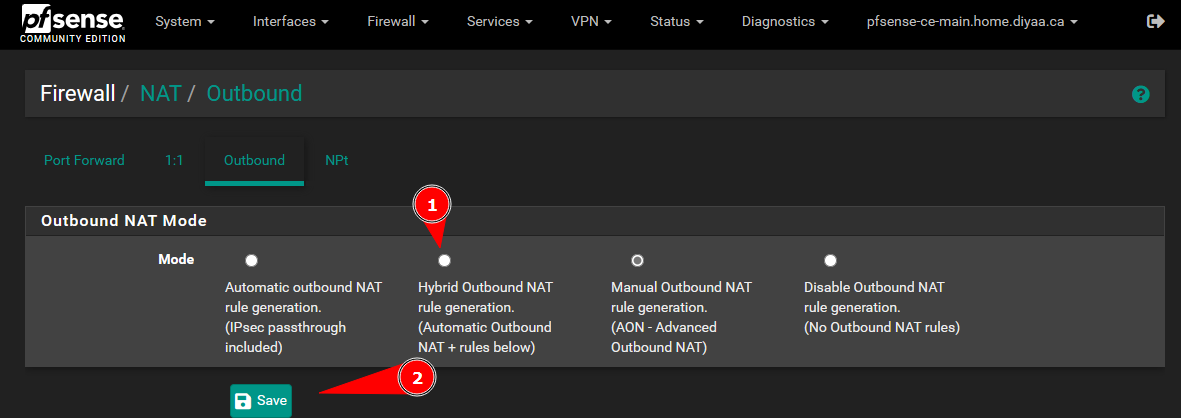
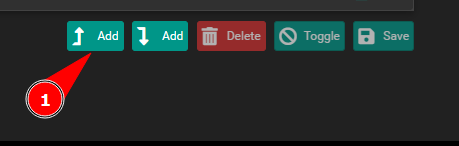
Scroll to the very bottom and you will see the arrow pointing upward at the bottom right of your screen. Click the button to create a new NAT rule and add it to the top of the NAT rulebase.
Create Access Control Rules on Pfsense:
Create a new firewall rule to utilize policy based routing over the WireGuard tunnel you created.
NOTE
You can customize the rule as you wish. I will be mostly pointing you to the steps of specifying the gateway on the rule (This is how you utilize policy based routing on Pfsense). I am adding this rule to the top of my rules. Feel free to change the positioning of the rule if you have a complex rulebase.
I will be placing this rule on the interface receiving inbound client traffic (client IP as source). You need to place the rule on the inbound interface where the client traffic will be coming from.
You will see the button for adding an access control rule at the bottom of the page with an arrow pointing upward. This will add the rule to the top of the rulebase making it match first.
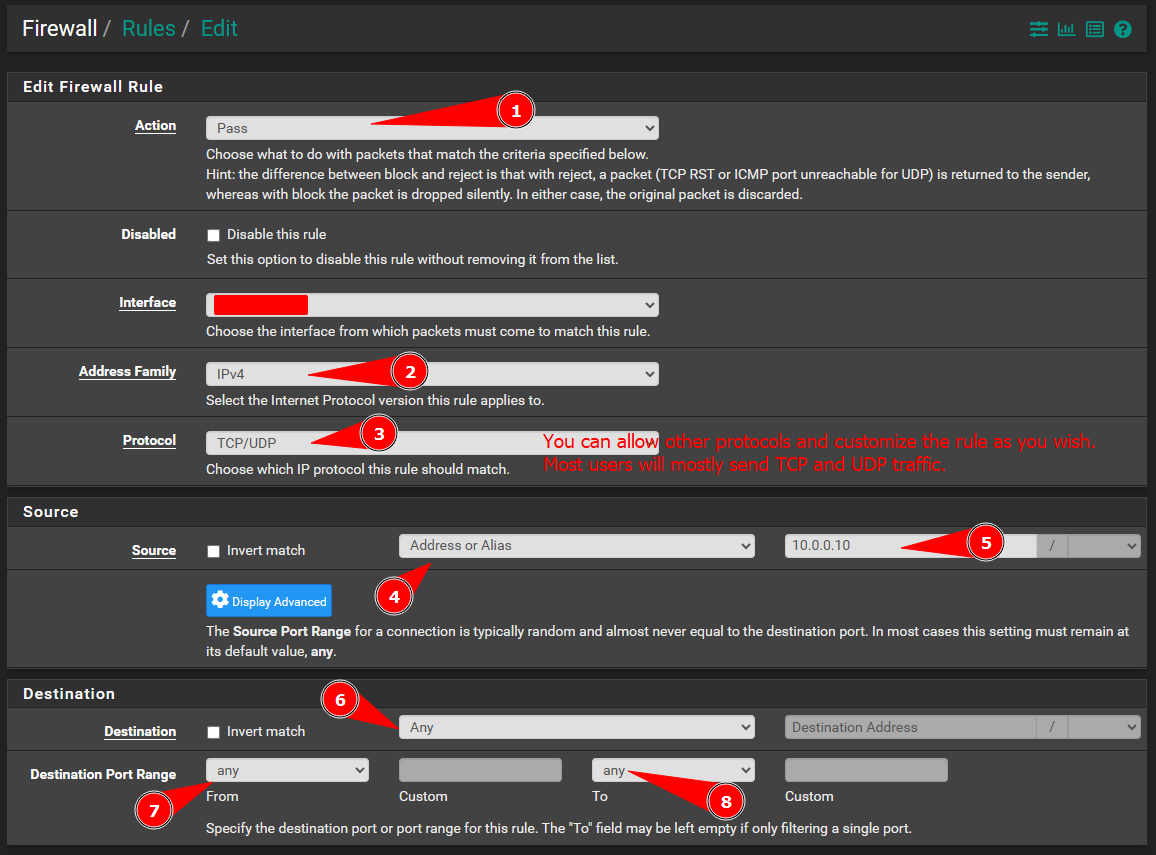
IMPORTANT
Configure the parameters in the rule. Do NOT save the rule just yet, there is more to configure… go to the next screenshot.
You will see an option above the save button “`Display Advanced”.
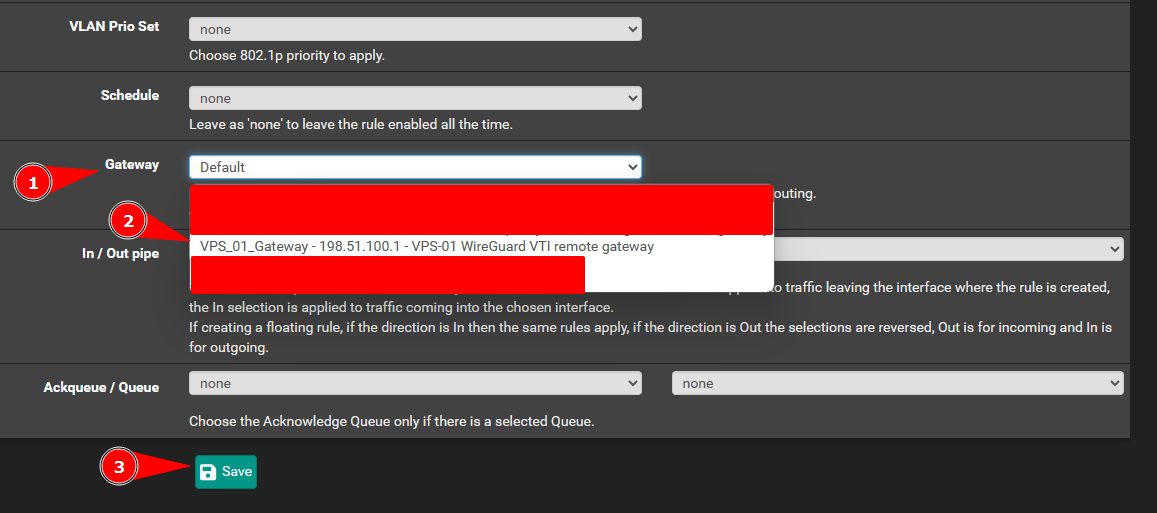
IMPORANT
You will have to apply the rules in Pfsense in order for the rule to take affect. You will see a pop up prompting you to apply the rules after you save the rule. You need to click the Apply button for the changes to take affect.
Scroll down until you find the Gateway option. Set the gateway to the VPS gateway you configured in the previous steps. Now you can save the rule.
Now you have configured policy based routing. However, we are not done yet…
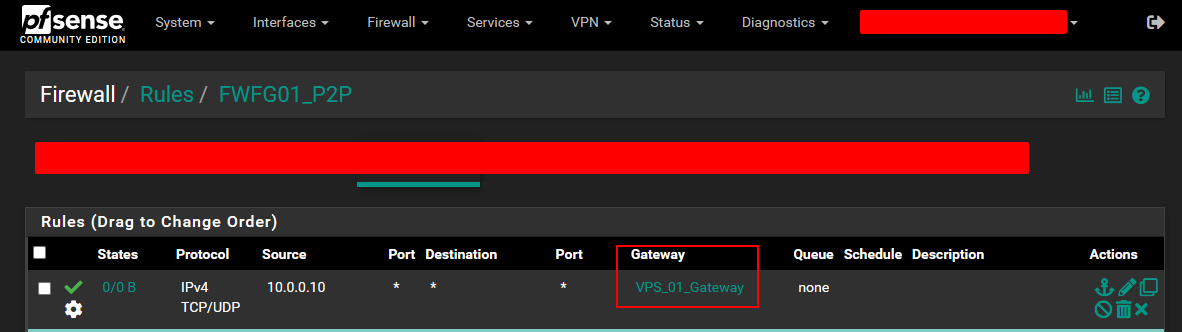
Recommended Rules Setup:
You can allow echo-request (ping) and add a deny rule under the rule in the step above to prevent traffic leak outside the VPN tunnel. This guarantees the host traffic will be going over the VPN tunnel only.
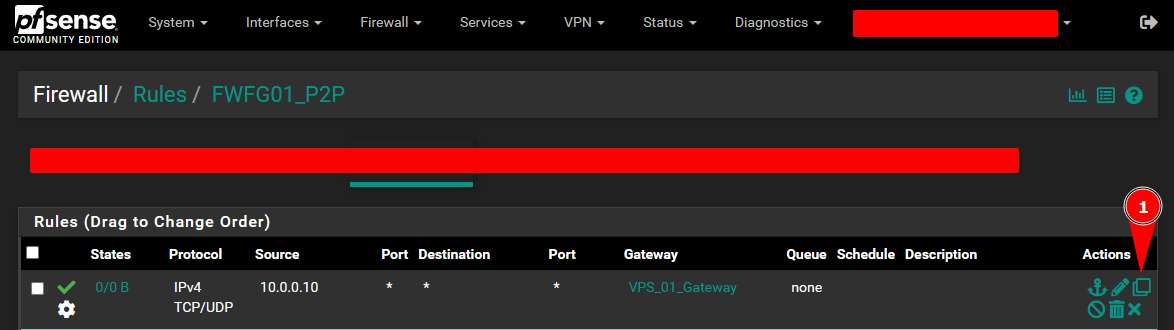
Clone the rule you created in the previous step.
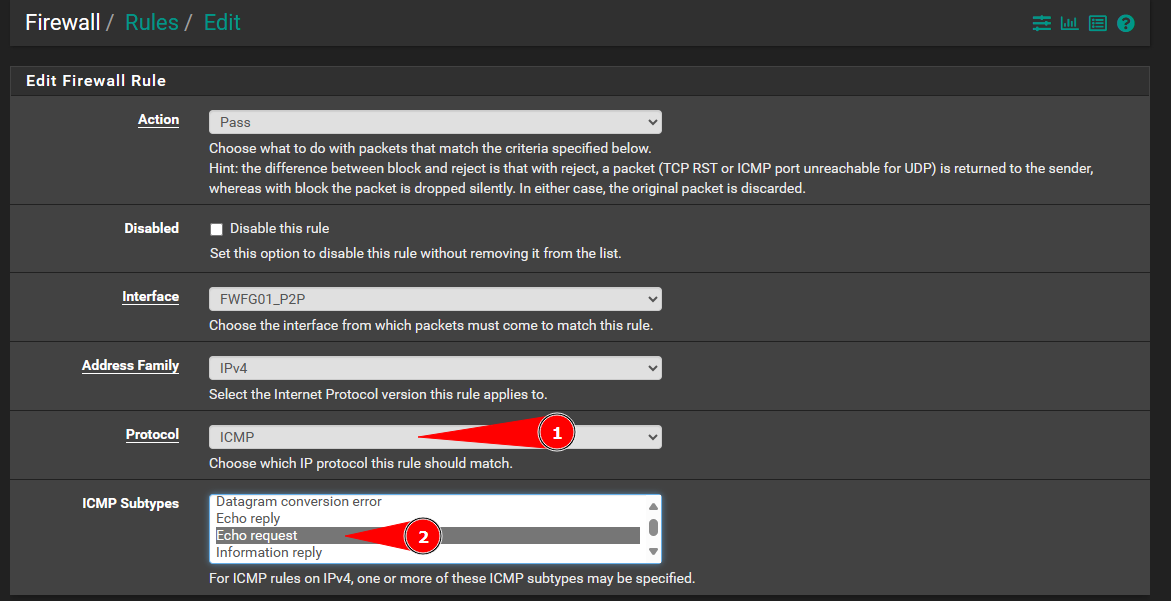
Change the protocol to ICMP and set the ICMP subtype to Echo request.
Note
This is to prevent any traffic that is not permitted in the top 2 rules from bypassing the policy based route.
Clone the second rule you created to create a drop rule.
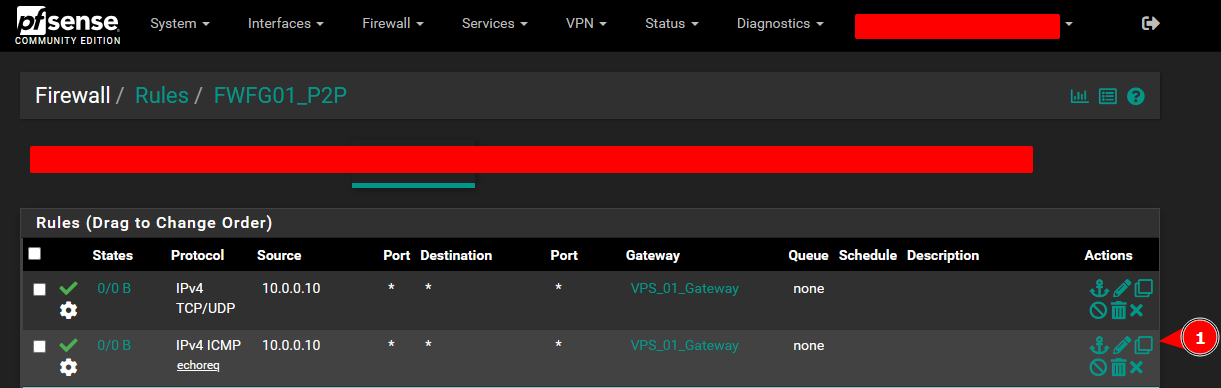
Set the action to Block and set the Protocol to Any.
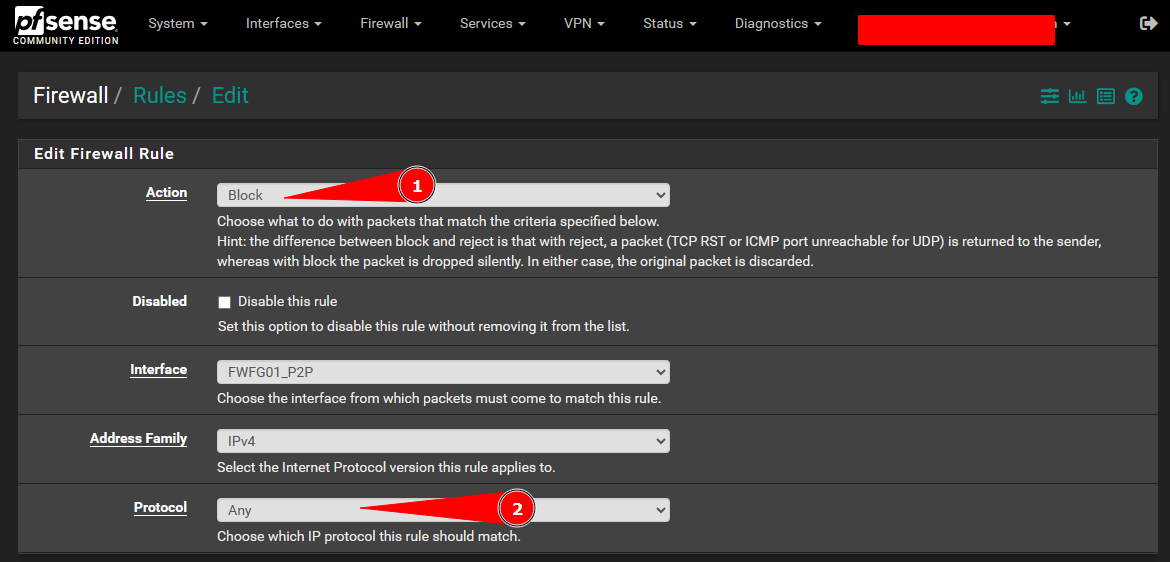
Change the Gateway option for the drop rule to Default and save the rule.
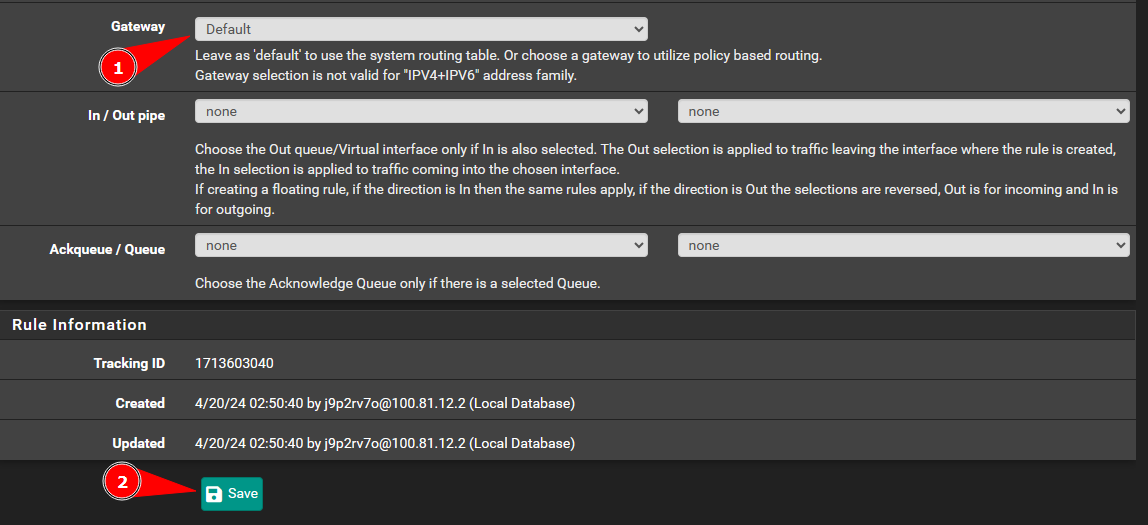
Your rules should look like this. The idea is to allow TCP, UDP, and echo-request. These are the most common traffic protocols that a host will utilize. The drop rule at the bottom will drop all other traffic. This prevents traffic leak outside the VPN tunnel.
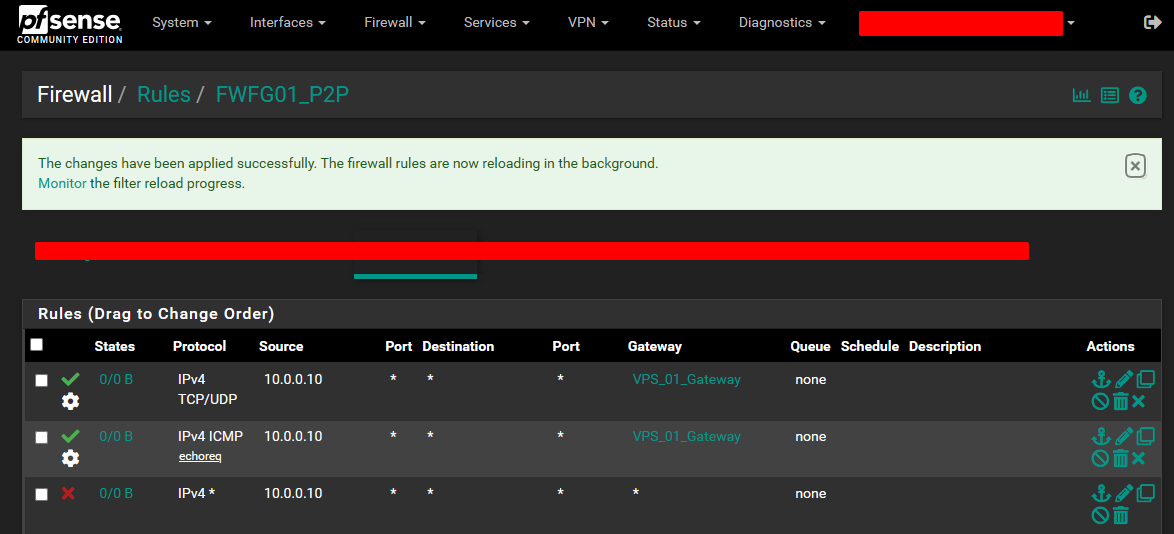
Finally, You have made it to the end. You are now utilizing policy based routing with Pfsense and WireGuard.
Related Notes:
- Link to Home-Page.
